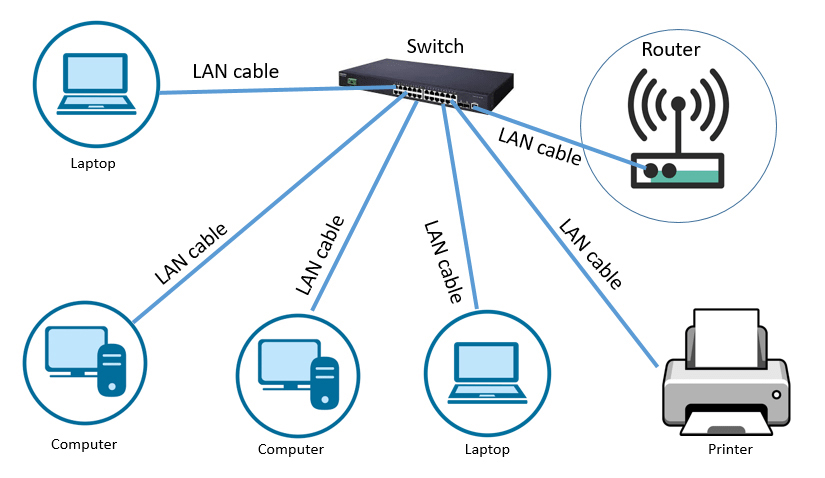
Local Area Network
Devices connected to each other in one physical location.
Wide area network
Connection of LAN's linked together around the world.

Virtual Private Network
Virtual Private Network overlay on a local network.
Local Area Network
Local Area Network (LAN) is a system where smart and IoT devices, like smart lighting system, video intercoms, smart sound systems, smart TVs, plus computers, laptops, printers and other devices connect to each other in one location. The scope of a LAN can range from few meters in a home to hundreds of meters in large company offices.
LAN use both wired and wireless connectivity options. Wireless LAN (WLAN) has surpassed traditional wired LAN in terms of popularity, but wired LAN remains more secure and reliable option. Wired LANs use physical cable like ethernet, fiber optic and switches, WLAN use devices like wireless routers and access points, to interconnect network devices through radio frequency waves.
LAN Benefits
Resource sharing is one of the most important reasons for setting up any network. As more devices connect to each other, they can share more files, data and software among each other.
Network data is stored in centralized location that all connected devices can access. Devices must receive permission to access the network, preventing unauthorized users from retrieving sensitive information.
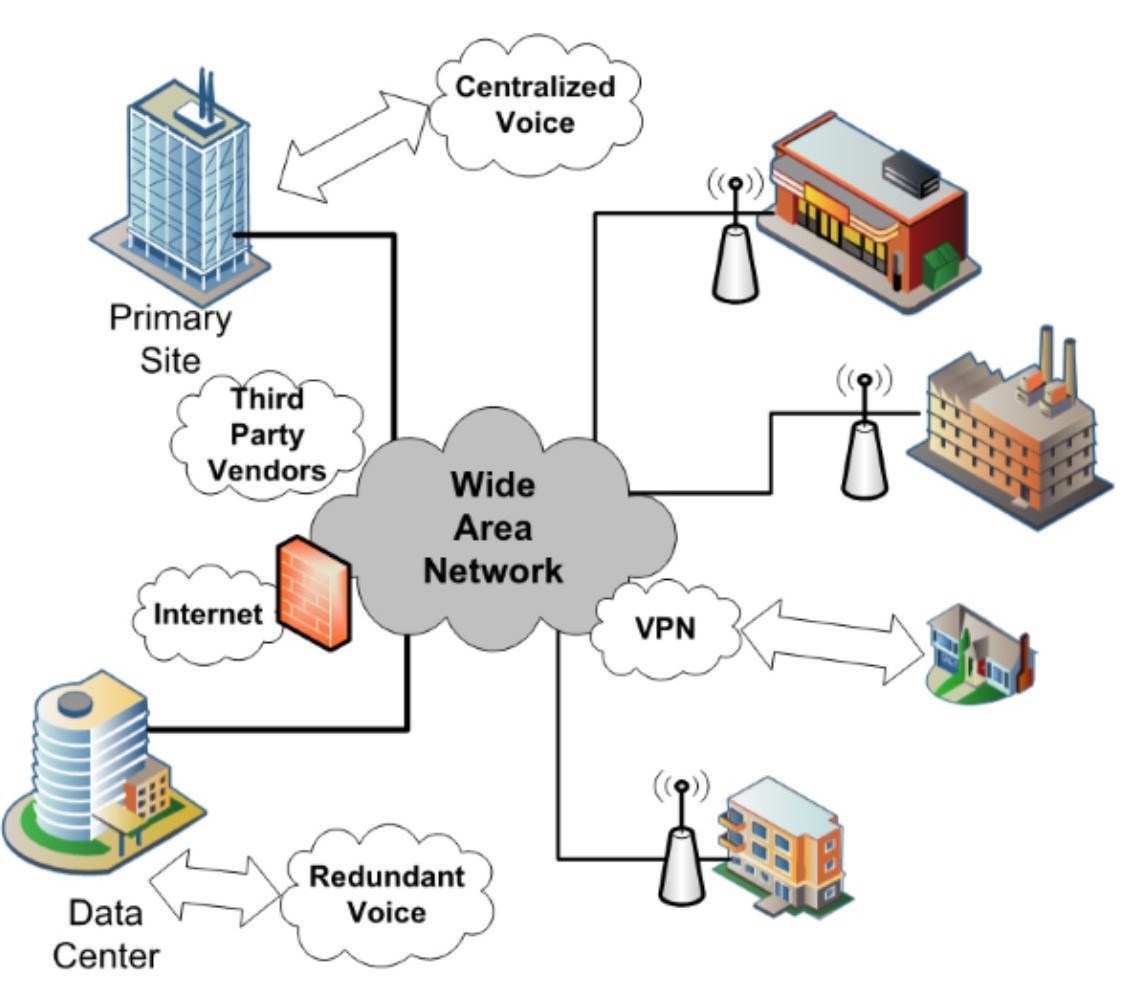
Wide Area Network
Wide Area Network (WAN) is a connection of multiple LANs belonging to the same network. WANs aren't restricted to the confines of city limits. A WAN can extend to any area of the globe. For example, an organization with a corporate office in New York can connect a branch location in London in the same WAN. Users in both locations obtain access to the same data, files and applications, and can communicate with each other.
WAN Benefits
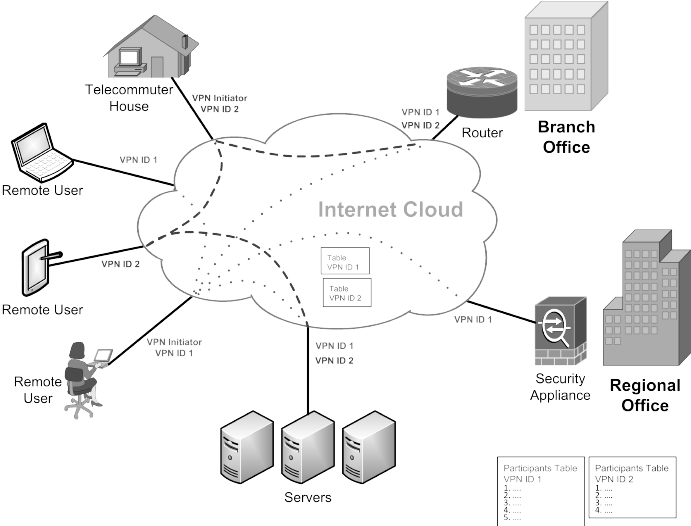
Virtual Private Network
A virtual private network (VPN) creates a private network overlay across an existing public network. VPNs use tunneling protocols that create encrypted connections between the network and client devices. Network traffic travels over the VPN service's secure, encrypted tunnels instead of a public network, effectively hiding a user's IP address and data from ISPs and cybersecurity hackers. The user's location appears to be wherever the VPN server exists.
VPN Benefits